The age-old debate in server management GUI vs CLI continues: visual interfaces versus command-line mastery, point-and-click simplicity versus keyboard-driven efficiency.
But here’s the truth about visual server management tools versus terminal SSH: it’s not an either/or choice. The best server administrators use both—leveraging GUI server management when it excels and dropping to the CLI terminal when it’s the superior option.
This comprehensive server management comparison helps you understand when to use visual tools like Server Explorer, when to reach for terminal SSH, and why having both at your disposal makes you a better system administrator. Whether you’re managing Docker containers, scheduling cron jobs, or performing security audits, this guide covers the strengths and weaknesses of each approach.
The Server Management GUI vs CLI Debate
“Real Developers Use the Terminal”
This gatekeeping attitude has plagued the tech industry for decades. The implication? If you prefer server management GUI tools, you’re somehow less competent than those using pure CLI.
The reality: Professional developers and sysadmins use whatever tool gets the job done efficiently. Using a visual server management interface doesn’t make you less technical—it makes you pragmatic, as explained in this comprehensive guide to modern DevOps practices.
Consider this:
- Do professional photographers only use manual camera settings? No—they use automatic modes when appropriate.
- Do professional designers hand-code every pixel? No—they use visual design tools.
- Do professional developers write assembly code for everything? No—they use high-level languages and IDEs.
Tools are tools. The mark of expertise is knowing which tool to use when.
What Server Explorer Actually Is
Before comparing, let’s be clear: Server Explorer isn’t a replacement for SSH terminals—it includes one.
Server Explorer is:
- A visual interface for common server management tasks
- An integrated SSH terminal for command-line work
- A bridge between GUI and CLI that lets you switch seamlessly
- A learning tool that shows you what commands do visually
Key insight: You’re not choosing between Server Explorer OR terminal SSH. You’re choosing between:
- Terminal SSH alone
- Server Explorer (which includes terminal SSH) + visual tools
When Server Explorer Excels
1. Visual File Management in Server GUI
Scenario: Navigate to /var/www/html/app/config/ and edit database.yml
Terminal SSH:
Copied!cd /var/www/html/app/config/ ls -la nano database.yml # Edit file # Remember to Ctrl+X, Y, Enter to save
Server Explorer (GUI approach):
- Click through directory tree
- Double-click
database.yml - Edit with syntax highlighting
- Ctrl+S to save
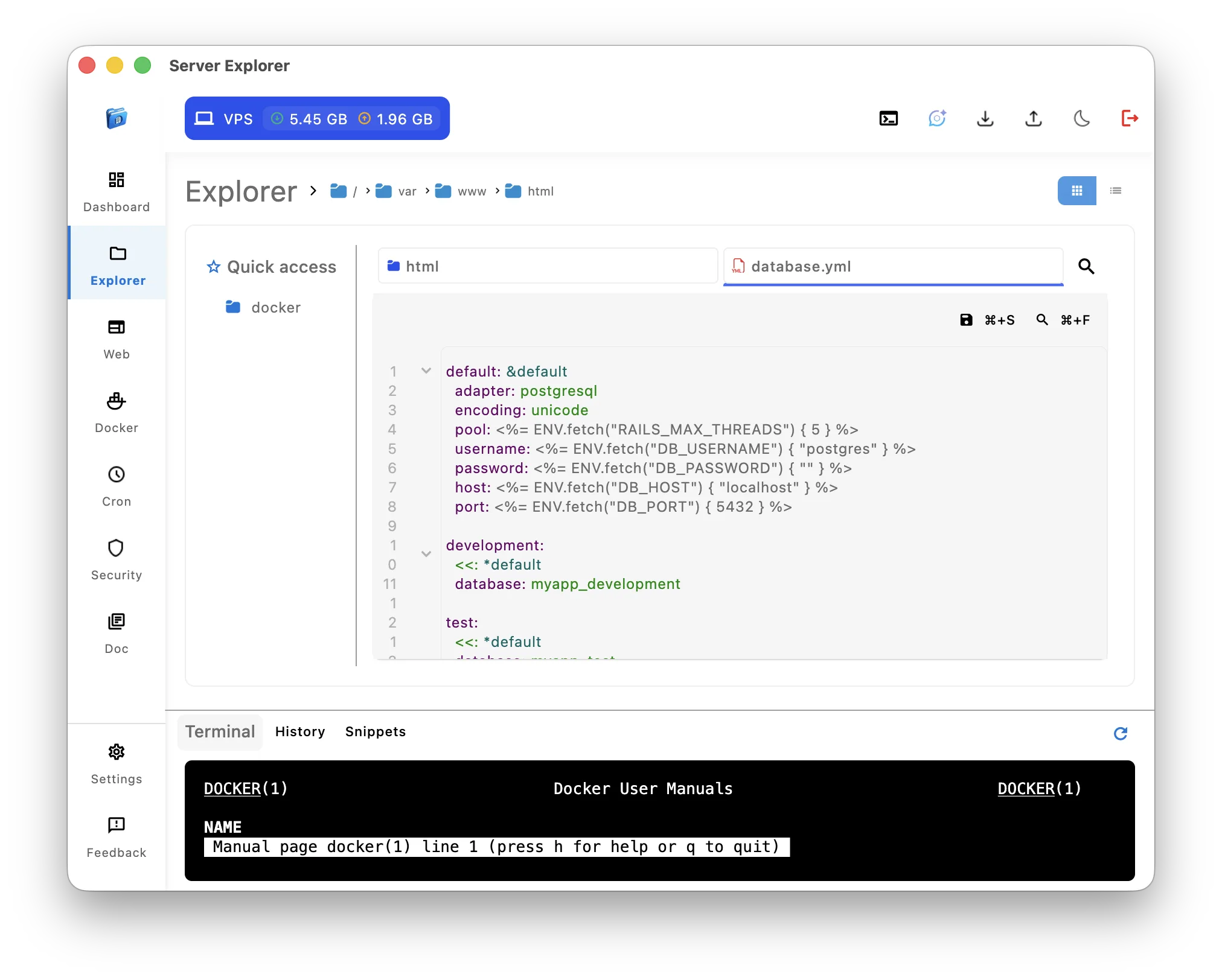
Winner: GUI Server Management ✅
Why:
- Visual directory browsing is faster for exploration
- Syntax highlighting prevents errors
- No need to remember editor commands
- Can see file permissions, sizes, dates at a glance
For more on effective file management strategies, see Linux file system best practices.
2. Server Monitoring: GUI Dashboard vs CLI Commands
Scenario: Check CPU, RAM, disk space, and running processes
Terminal SSH:
Copied!top # Exit, then: free -h # Exit, then: df -h # Exit, then: ps aux | grep node # Mental gymnastics to correlate all this data
Server Explorer GUI: Dashboard shows all at once:
- CPU usage graph
- Memory consumption
- Disk space by partition
- Active processes
- Network activity

Winner: Visual Server Management ✅
Why:
- Parallel visibility beats sequential checking
- Graphs show trends over time
- No context switching between commands
- Correlate metrics instantly (e.g., which process is using CPU)
3. Docker Container Management: GUI vs Terminal
Scenario: View all containers, check logs, restart one
Terminal SSH:
Copied!docker ps -a # Copy container ID or name docker logs -f container_name # Ctrl+C to exit logs docker restart container_name docker ps | grep container_name # Verify it restarted
Server Explorer GUI:
- Open Docker section
- See all containers with status
- Click container → Logs tab (live stream)
- Click Restart button
- Status updates automatically
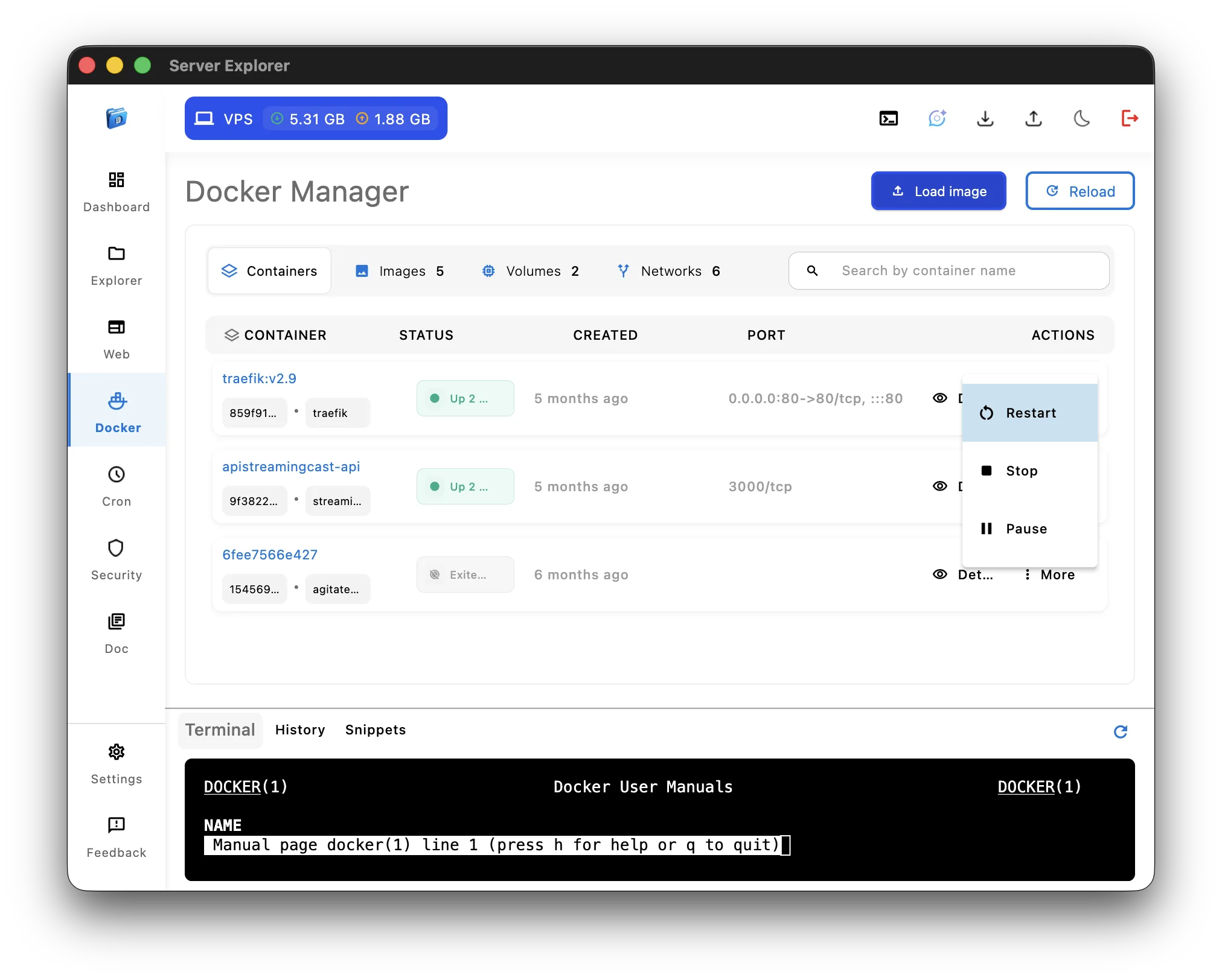
Winner: GUI Server Management ✅
Why:
- All information in one view
- No copying container IDs
- Live updates without manual refreshing with the widget on the dashboard
- Point-and-click operations for common tasks
For more on Docker best practices and container orchestration, check the official documentation.
4. VPS Security Auditing: Visual Scanning vs Manual CLI
Scenario: Comprehensive security check of your server
Terminal SSH:
Copied!# Check firewall sudo ufw status verbose # Check SSH config sudo grep -E 'PermitRootLogin|PasswordAuthentication' /etc/ssh/sshd_config # Check open ports sudo ss -tulpn # Check fail2ban sudo fail2ban-client status # Check pending updates sudo apt list --upgradable # Check sudo users sudo grep -Po '^sudo.+:\K.*
Performing a complete audit manually means running more than a dozen commands, reading verbose outputs, cross-checking configurations, and visually correlating vulnerabilities. This is error-prone, slow, and easy to forget if you’re not doing it daily.
Server Explorer Security Scanner:
- Open Security section
- Click Run Scan
- Review the 18 automated checks
- Click any issue to get remediation steps
- Apply recommended fixes directly via integrated terminal
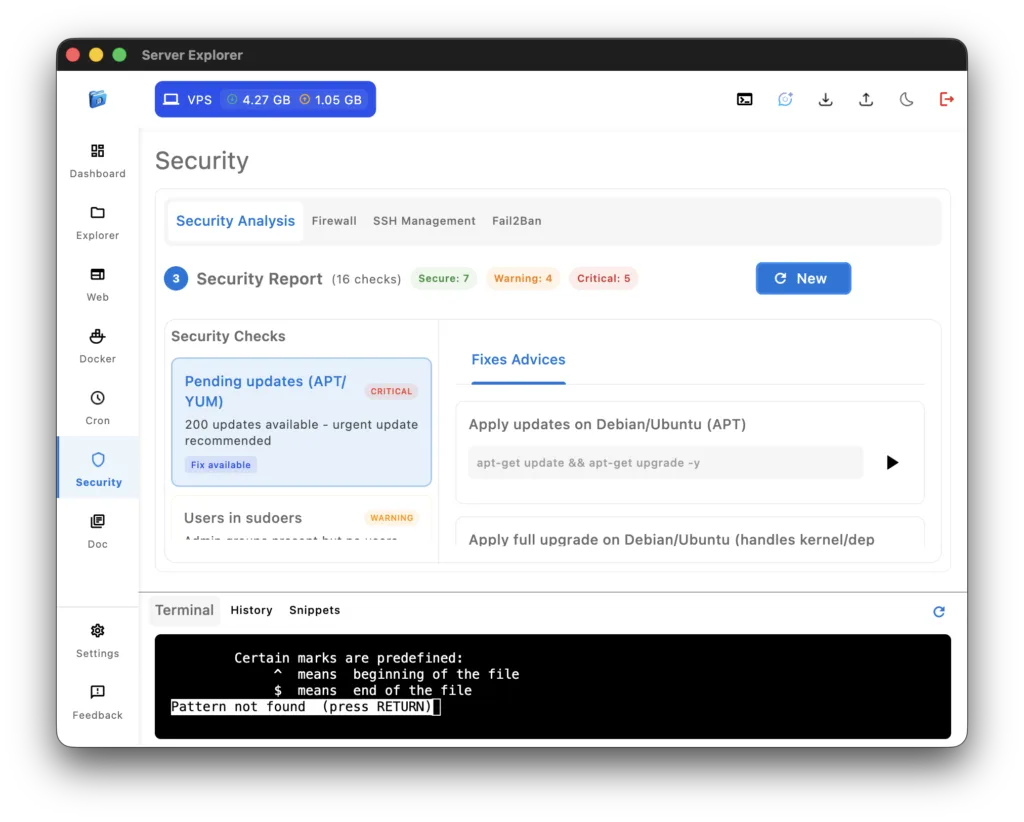
Winner: Visual Server Management ✅
Why it matters:
- One click instead of 20+ commands
- All checks grouped and prioritized
- Critical, warning, and OK states clearly color-coded
- Built-in explanations and step-by-step fixes
- Zero memorization of security commands
This is especially valuable in production environments where overlooking a single SSH configuration or forgotten firewall rule can expose the entire server.
5. Cron Job Management: Visual Scheduler vs Crontab
Scenario: Create a daily backup script scheduled for 3 AM
Terminal SSH:
Copied!crontab -e # Syntax: minute hour day month weekday # 0 3 * * * /home/user/backup.sh # Did I mix the order? Need to check again... # No feedback if syntax is invalid
Managing cron via CLI is powerful but unforgiving. Syntax errors fail silently, typos can break tasks, and even experienced admins check reference tools like crontab.guru.
Server Explorer:
- Open Cron
- Click + New
- Pick your script
- Choose Every day
- Select 03:00
- Save
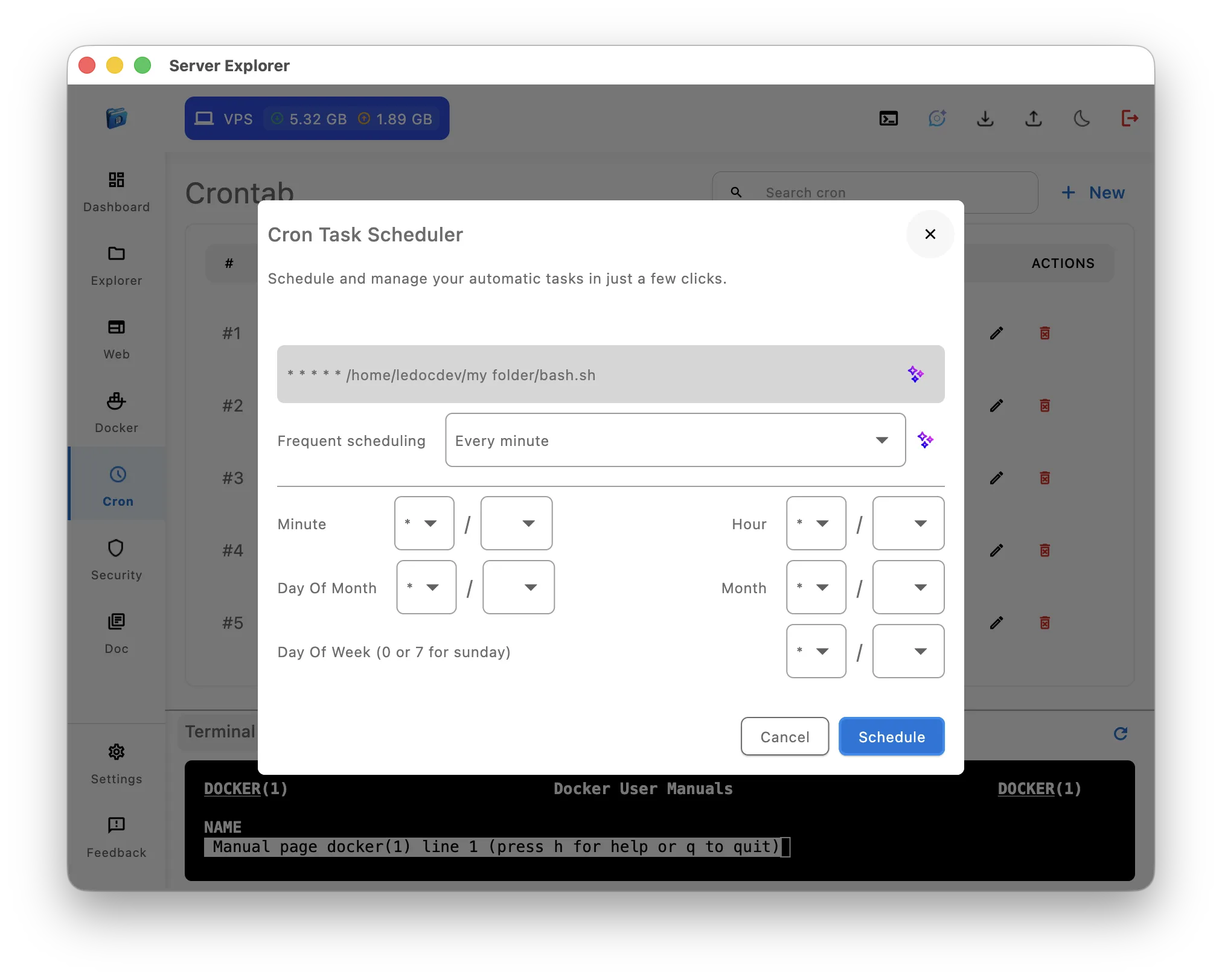
Winner: Server Explorer ✅
Why:
- No syntax to memorize
- View all scheduled tasks at once
- Easy modification and deletion
- Perfect for repeated maintenance tasks
Cron is one of the most error-sensitive parts of server management, so adding a visual layer drastically reduces breakage.
6. Learning Linux Administration
Scenario: You’re new to Linux and managing your first VPS
Terminal SSH:
- Steep learning curve
- High risk of destructive mistakes
- Minimal visual feedback
- Hard to understand system structure
- Every command feels like unknown territory
Server Explorer:
- Shows full file structure visually
- Process lists, Docker containers, cron jobs, and logs all visible
- Integrated terminal allows learning at your pace
- Reduces fear of breaking things
- Encourages exploration with context
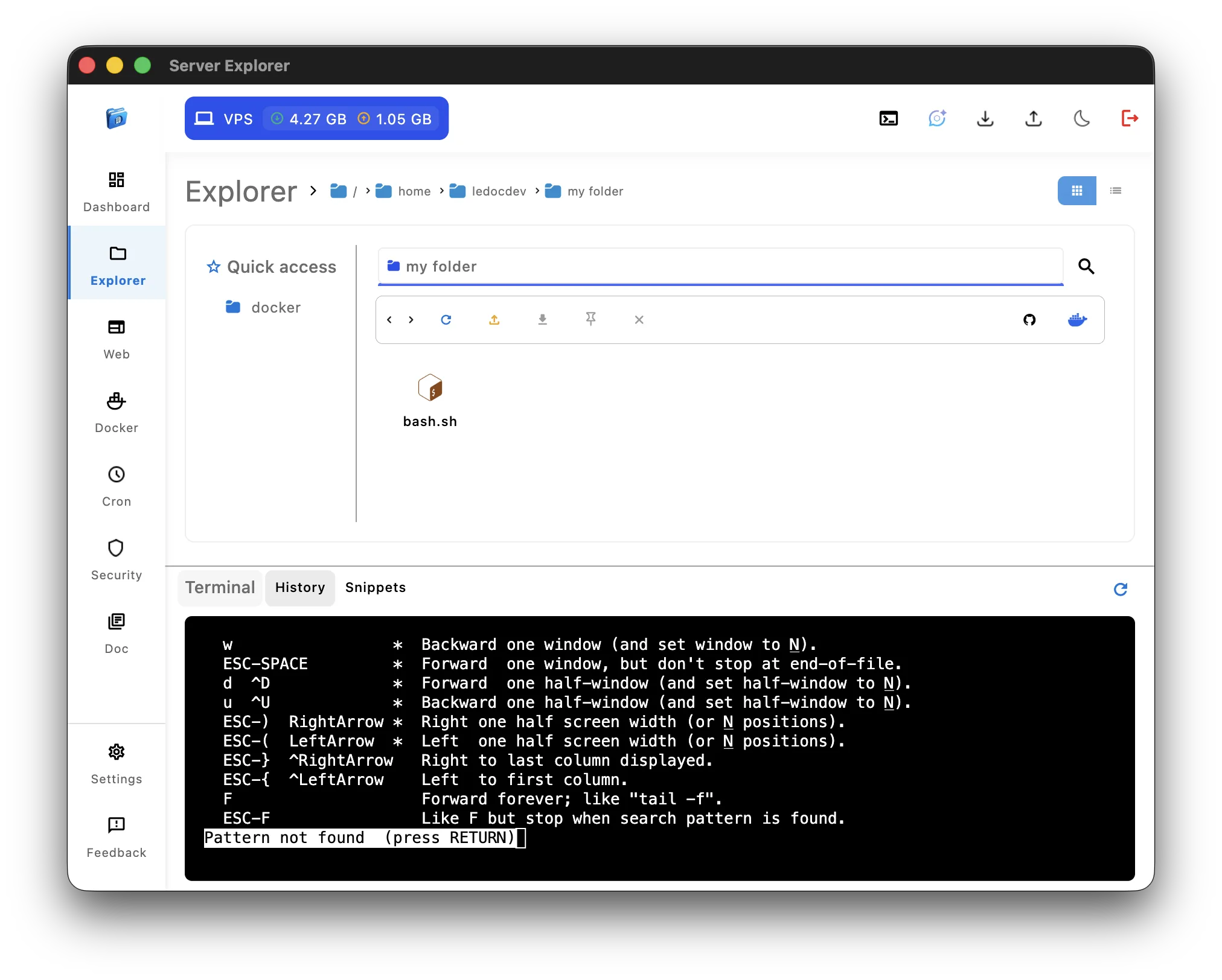
Winner: Server Explorer for beginners ✅
Why:
- Visual context builds intuition
- Ideal as a stepping stone to mastering SSH
When CLI Terminal Wins the Server Management Battle
1. Bulk Operations and Scripting
Scenario: Restart all containers matching a naming pattern
Terminal SSH:
Copied!docker ps | grep api- | awk '{print $1}' | xargs docker restart
Server Explorer:
Select each container manually → Restart
Winner: Terminal SSH ✅
Why it wins:
- Command pipelines handle patterns instantly
- Perfect for repetitive or large batch operations
- Fully scriptable and automatable
- Can be saved and reused across servers
For deeper scripting techniques, see the official GNU Bash manual.
2. Complex Text Processing
Scenario: Extract error logs from the last hour and count specific occurrences
Terminal SSH:
Copied!grep -i "error" /var/log/app.log | \ grep "$(date -d '1 hour ago' '+%Y-%m-%d %H')" | \ grep "database connection" | \ wc -l
Server Explorer:
Manual scanning and filtering of logs
Winner: Terminal SSH ✅
Why it wins:
- grep, awk, and sed excel at high-precision filtering
- Pipe chains allow multi-layered transformations
- Regex makes it extremely efficient
- Handles huge logs faster than any GUI
3. Git Operations
Scenario: Pull latest changes, inspect status, commit and push updates
Terminal SSH:
Copied!cd /var/www/app git pull origin main git status git add . git commit -m "Update configuration" git push
Server Explorer:
Requires the integrated terminal or an external Git client
Winner: Terminal SSH ✅
Why it wins:
- Git is a CLI-first tool
- Complex workflows (merges, rebases, conflict resolution) require commands
- Fits naturally into deployment pipelines
- Fast, precise, and scriptable
4. Package Installation
Scenario: Install software with specific flags and dependencies**
Terminal SSH:
Copied!sudo apt update sudo apt install nginx -y sudo apt install php8.1-fpm php8.1-mysql php8.1-curl
Server Explorer:
Uses the same terminal for installation
Winner: Terminal SSH ✅ (functionally a tie)
Why it wins:
- Package managers are designed for CLI
- Many flags and options rely on command syntax
- Faster for chaining multiple installs
- Terminal gives full control over dependency handling
5. Remote Fixes from Mobile or Tablet
Scenario: Urgent issue while away from your computer
Terminal SSH:
Use a mobile SSH app like Termius, iSH, or JuiceSSH
Copied!# Works from any device supporting SSH
Server Explorer:
Requires the desktop application
Winner: Terminal SSH ✅
Why it wins:
- Accessible from any phone or tablet
- Lightweight and fast over weak connections
- Perfect for emergencies
- No desktop dependency
6. Automation and CI/CD Pipelines
Scenario: Automated deployment or maintenance script
Terminal SSH (script):
Copied!#!/bin/bash ssh user@server << 'EOF' cd /var/www/app git pull npm install pm2 restart app EOF
Server Explorer:
Not intended for scripted or non-interactive automation
Winner: Terminal SSH ✅
Why it wins:
- Automation requires predictable, text-based commands
- Ideal for pipelines, hooks, cron-driven scripts
- Integrates seamlessly with GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, Jenkins, etc.
- No GUI layer needed for unattended execution
| Task | Terminal SSH | Server Explorer GUI | Winner |
| File browsing |
cd, ls commands |
Visual tree & list | GUI |
| Edit config file |
nano/vim
|
Built-in editor | GUI |
| Check disk space | Dashboard widget | Live log viewer | GUI |
| View processes |
top, ps aux
|
Dashboard + PM2 section | GUI |
| Docker logs | docker logs -f |
Live log viewer | GUI |
| Security audit | 15+ commands | One-click scan | GUI |
| Cron schedule | crontab -e |
Visual scheduler | GUI |
| Git operations |
git commands |
Terminal needed | CLI |
| Bulk text processing |
grep/awk/sed
|
Manual | CLI |
| Package install |
apt/yum
|
Terminal needed | CLI |
| Script execution | Direct execution | Terminal needed | CLI |
| Automation/CI-CD | SSH scripts | Not designed for this | CLI |
| Emergency mobile access | Mobile SSH apps | Desktop only | CLI |
| Learn Linux | Steep curve | Visual learning | GUI |
| System monitoring | Sequential commands | Parallel dashboard | GUI |
Score: Visual Server Management 9 | CLI Terminal 6
But this isn’t about winning—it’s about using the right tool for each job.
Conclusion: The Best Tool Is the One You’ll Actually Use
The terminal vs GUI debate is a distraction from what matters: effectively managing servers.
The truth:
- Terminal SSH is powerful and universal
- Server Explorer provides visual efficiency and safety
- Both have legitimate use cases
- The best approach is hybrid
Choose based on:
- Your skill level (beginners benefit more from GUI)
- The specific task (some tasks suit CLI, others GUI)
- Your workflow (optimize for your common operations)
- Your team (visual tools ease collaboration)
Remember: You’re not choosing between tools—you’re choosing whether to limit yourself to one tool or have access to both.
Server Explorer includes a terminal. You lose nothing by having visual tools available. You gain efficiency for tasks where visualization helps.
The real question isn’t “Which should you use?”—it’s “Why limit yourself to just one?”
Get the Best of Both Worlds
Ready to combine the power of terminal SSH with modern visual management?

Server Explorer
Manage your servers with just a few clicks. Replace complex command-line operations with an intuitive interface, while maintaining the performance and security of traditional SSH access.
Server Explorer gives you:
✅ Full SSH terminal access (never locked out of CLI)
✅ Visual dashboard for parallel monitoring
✅ Point-and-click container management
✅ Automated security scanning
✅ File browser with syntax highlighting
✅ Cron scheduler with visual validation
✅ Choose the right tool for each task
✅ Learn gradually without pressure
Stop debating. Start using both.
Server Explorer is available now for macOS and Windows. Get the flexibility of terminal SSH with the efficiency of visual tools at serverexplorer.ledocdev.com