You don’t need to memorize terminal commands to manage Linux servers via SSH.
For decades, SSH has been synonymous with black terminals, cryptic commands, and steep learning curves. But SSH without terminal interfaces is not only possible—it’s often more efficient for daily server management tasks.
Modern visual SSH tools provide graphical interfaces for file management, process monitoring, Docker containers, and security—all over secure SSH connections. You still leverage SSH’s security and power, but through intuitive visual workflows instead of command memorization.
This guide explores SSH GUI alternatives that let you manage Linux servers visually while maintaining the security and control of traditional SSH access. Whether you’re a developer tired of terminal fatigue or a beginner intimidated by command-line interfaces, these tools transform how you interact with remote servers.
Why SSH without Terminal Is Possible Today
SSH (Secure Shell) is a protocol, not a user interface.
Most people associate SSH with terminal windows because that’s how it was traditionally accessed. But SSH is fundamentally about secure remote connections—how you interact with that connection is flexible.
Understanding SSH without Terminal vs Traditional Command Line
SSH provides:
- Encrypted connection to remote server
- Authentication (password or keys)
- Secure data transfer
- Command execution capabilities
- File transfer protocols (SFTP)
Terminal provides:
- Command-line interface
- Text-based interaction
- Shell access (bash, zsh, etc.)
These are separate concepts. You can have SSH without terminal, just as you can have terminal without SSH (local shell).
The Terminal-Only Myth
Many developers believe they must use terminal for SSH because:
❌ “SSH means terminal” (no—SSH is the protocol)
❌ “GUI tools are less secure” (no—they use the same SSH)
❌ “Real admins use terminal” (gatekeeping, not reality)
❌ “Visual tools hide what’s happening” (modern tools show everything)
❌ “Terminal is faster” (depends on the task)
The reality: Visual SSH tools use the exact same SSH protocol as terminal, with identical security. They simply provide a graphical layer on top of SSH commands.
Why Visual SSH Makes Sense
For many common server tasks, visual interfaces are:
✅ Faster – Click vs. remembering command syntax
✅ Safer – Visual confirmation before destructive operations
✅ More discoverable – See available options
✅ Lower cognitive load – Reduce mental overhead
✅ Better for learning – Understand file structures visually
✅ More efficient – Parallel information display
You’re not avoiding SSH—you’re using it more effectively.
For context on SSH protocol fundamentals, SSH Academy provides excellent technical resources.
What Visual SSH Tools Do to Enable SSH without Terminal
Visual SSH tools connect to your Linux server via SSH and provide graphical interfaces for common tasks.
How They Work
Traditional SSH workflow:
Copied!Your Computer → SSH Protocol → Linux Server ↓ Terminal Window ↓ Type commands ↓ See text output
Visual SSH workflow:
Copied!Your Computer → SSH Protocol → Linux Server ↓ Visual Application (GUI) ↓ Click, drag, select ↓ See graphical output
Behind the scenes, visual tools still execute SSH commands—you just don’t see or type them.
What Gets Installed Where
Important: Visual SSH tools run on your local computer, not the server.
On your computer:
- Visual SSH application (Server Explorer, Termius, etc.)
- GUI interface
- Local file cache (temporary)
On your server:
- Nothing additional installed
- Just standard SSH server (already there)
- Same security as terminal SSH
This means:
- No server modifications needed
- No additional security risks
- Works with any Linux server with SSH access
- Can uninstall visual tool without affecting server
What Visual Tools Replace
Visual SSH alternatives can replace or supplement:
File management:
-
cd,ls,mkdir→ Visual file browser -
nano,vim→ Graphical editor with syntax highlighting -
chmod,chown→ Visual permission settings -
scp,rsync→ Drag-and-drop or Files uploads
Process monitoring:
-
top,htop→ Dashboard with graphs -
ps aux→ Visual process list -
free -h→ Memory usage charts -
df -h→ Disk space visualization
Service management:
-
systemctl status→ Service status indicators -
docker ps→ Container list with controls -
pm2 list→ Process manager interface
Security:
- 15+ security check commands → One-click security scan
- Manual auditing → Automated vulnerability detection
Core Features That Make SSH without Terminal Work
What should you expect from a modern visual SSH tool?
1. Visual File Browser
Replace: cd, ls, pwd, find
Visual equivalent:
- Tree view of directory structure
- Grid/list view of files
- Text editor
- Search across filesystem
- Breadcrumb navigation
- Favorites/bookmarks
Benefits:
- See directory structure at a glance
- Navigate like Windows Explorer or macOS Finder
- No memorizing paths
- Visual feedback on file sizes, dates, permissions
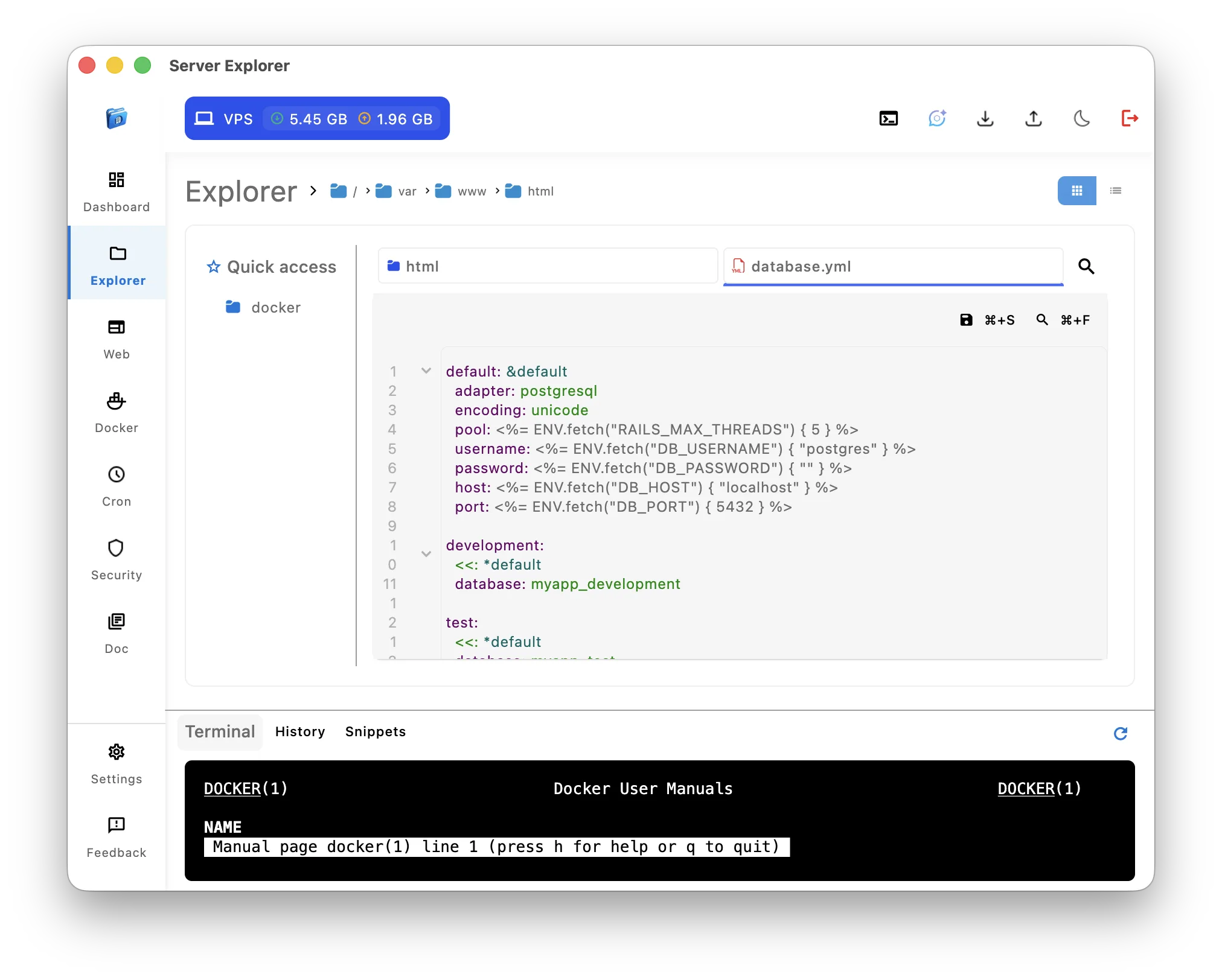
2. Integrated File Editor
Replace: nano, vim, emacs
Visual equivalent:
- Click file to open
- Syntax highlighting for common languages
- Code completion suggestions
- Find and replace
- Multiple files in tabs
- Save directly (Ctrl+S)
Benefits:
- Edit server files like local files
- No download-edit-upload cycle
- Syntax highlighting prevents errors
- Modern editor features (find, replace, multiple cursors)
3. Server Dashboard
Replace: top, free, df, uptime, netstat
Visual equivalent:
- CPU usage graph (real-time)
- RAM consumption chart
- Disk space by partition
- Network activity
- System uptime
- Load averages
Benefits:
- See everything at once (no sequential commands)
- Trends over time (graphs vs snapshots)
- Color-coded alerts (red = problem)
- No parsing text output

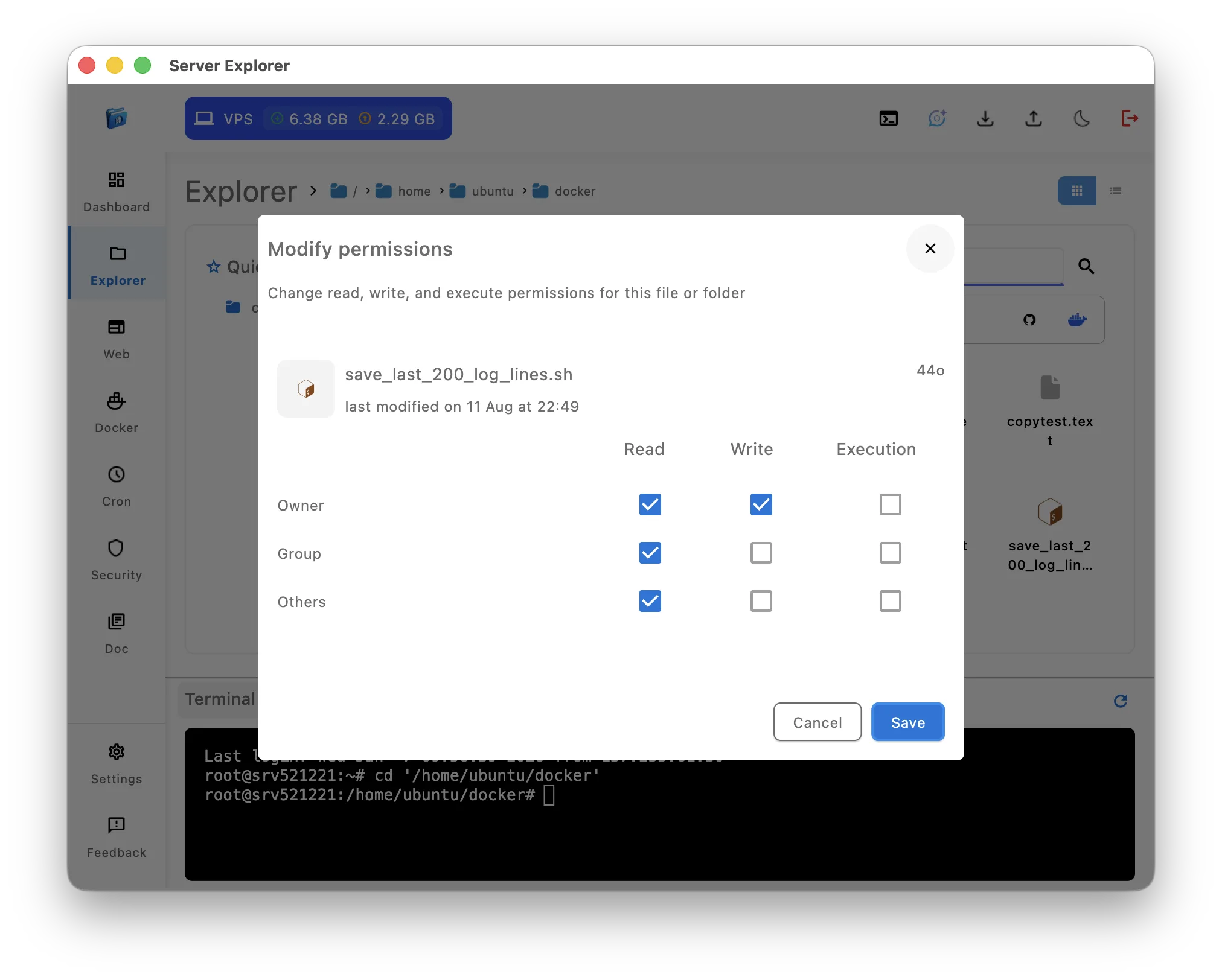
4. Visual Permission Management
Replace: chmod 755 file.sh, chown user:group file.txt
Visual equivalent:
- Right-click file → Permissions
- Checkboxes: Read, Write, Execute
- Owner/Group dropdowns
Benefits:
- No memorizing numeric codes
- Visual confirmation of changes
- See current permissions clearly
- Understand what you’re changing
5. Integrated Terminal (Hybrid Approach)
Best visual SSH tools include terminal access for when you need it:
- Run custom commands
- Execute scripts
- Install packages
- Perform complex operations
This gives you:
- Visual tools for routine tasks
- Terminal for advanced operations
- Best of both worlds
- Gradual learning path

6. Multi-Server Management
Replace: Multiple terminal windows, screen/tmux sessions
Visual equivalent:
- Server list
- Organize by group
Benefits:
- Manage 10+ servers easily
- No confusion about which terminal connects where
- Quick context switching
- Visual overview of all servers
Best Visual SSH Tools for SSH without Terminal on Linux Servers
Several excellent visual SSH alternatives exist for different platforms and needs.
Comparison Table
| Tool | Platform | Price | Best For | File Management | Server Dashboard |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Server Explorer | Windows, macOS | Paid | Complete server management | ✅ Advanced | ✅ Real-time |
| Termius | All platforms | Free/Paid | Mobile + desktop sync | ✅ Basic | ❌ |
| Royal TSX | macOS, Windows | Paid | Enterprise multi-protocol | ⚠️ Limited | ⚠️ Limited |
| MobaXterm | Windows | Free/Paid | Power users, X11 | ✅ Sidebar | ⚠️ Basic |
| Transmit | macOS | Paid | Mac-native SFTP | ✅ Advanced | ❌ |
| Cyberduck | Windows, macOS | Free | Simple file transfer | ✅ Basic | ❌ |
Quick Recommendations
For comprehensive server management:
→ Server Explorer (files, monitoring, Docker, security)
For cross-platform file management:
→ Termius (mobile support)
For Mac users wanting file transfer:
→ Transmit (beautiful, Mac-native)
For Windows power users:
→ MobaXterm (feature-packed)
For simple SFTP needs:
→ Cyberduck (free, simple)
Related: Best SSH GUI Tools for Linux and Windows (2026 Edition)
Server Explorer: Complete SSH without Terminal Management
Server Explorer provides the most comprehensive visual alternative to terminal SSH, designed specifically for developers and sysadmins managing Linux VPS servers.
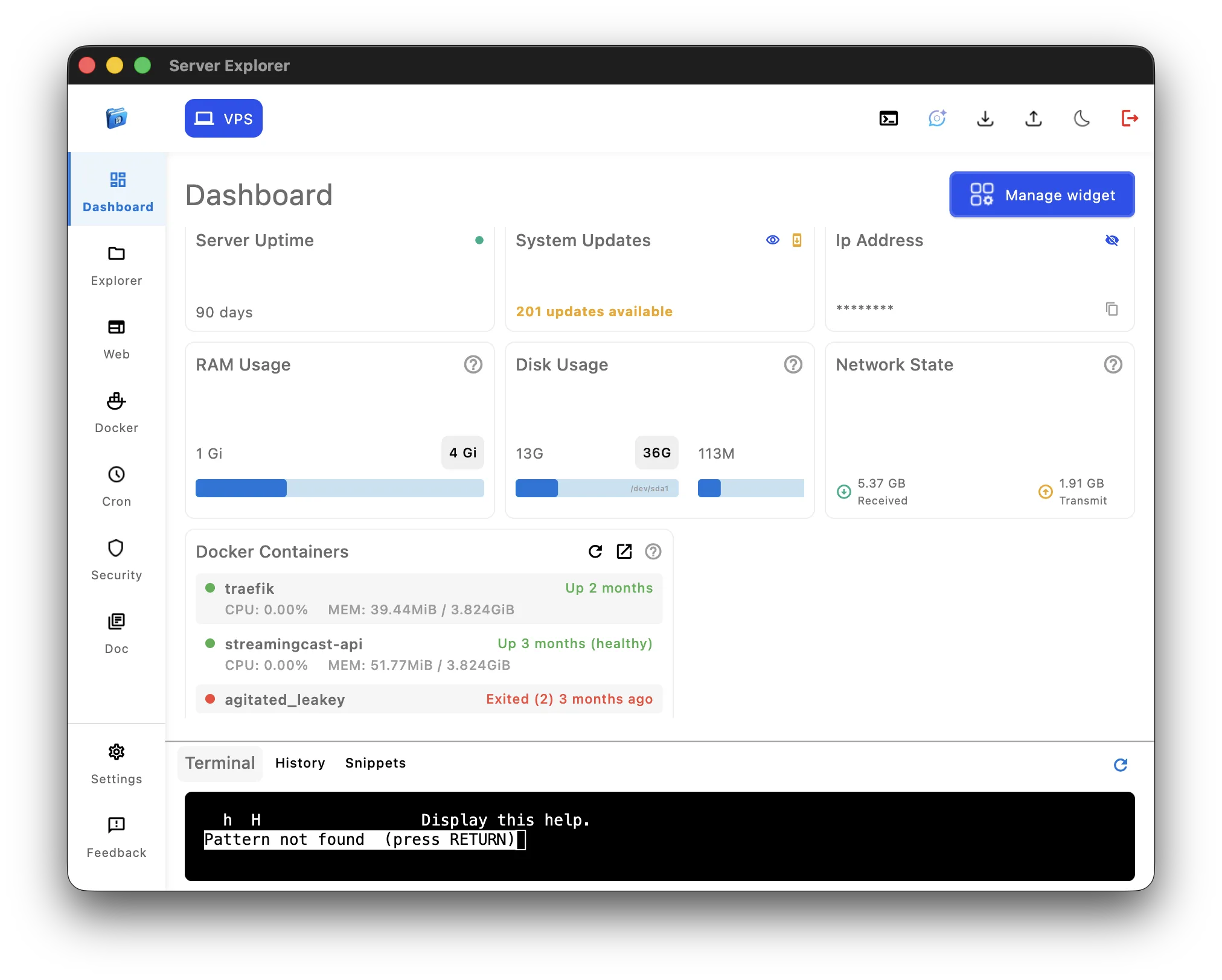
What Server Explorer Provides
File Management:
- Visual browser (tree + list view)
- Direct file editing with syntax highlighting
- Drag-and-drop upload/download
- Visual permission management
- Search entire filesystem
Server Monitoring:
- Real-time CPU/RAM/disk graphs
- Process list with resource usage
- Network activity tracking
Docker Management:
- Container list with status
- Start/stop/restart controls
- Live log streaming
- Container filesystem browser
- Image, volume, network management
PM2 Process Management:
- Node.js application monitoring
- Restart services with one click
- Live application logs
- CPU/memory per process
Security Tools:
- Security scanner (18 checks)
- SSH configuration audit
- Firewall status
- Open port analysis
- Pending security updates
- Step-by-step remediation guides
Cron Job Scheduler:
- Visual cron builder (no syntax needed)
- Schedule backups, cleanups, updates
- See all scheduled tasks
Integrated Terminal:
- Full SSH terminal when needed
- Command history
- Copy paths from file browser
- Terminal + visual tools side-by-side
Why Server Explorer Excels at SSH without Terminal
1. Complete solution – Not just files or just terminal, everything integrated
2. Real-time updates – Dashboard refreshes automatically
3. No server installation – Pure SSH client, nothing installed remotely
4. Modern UI – Designed for recent workflows
5. Learning tool – Helps you understand Linux visually
6. Time-saving – Common tasks are point-and-click
Server Explorer Workflow Example
Traditional terminal SSH workflow:
Copied!# Check disk space df -h # Navigate to app directory cd /var/www/app # Edit configuration nano config.yml # Save and exit nano (Ctrl+X, Y, Enter) # Restart service sudo systemctl restart app # Check if it worked sudo systemctl status app # View logs sudo journalctl -u app -n 50
Server Explorer visual workflow:
Copied!1. Open Server Explorer → See dashboard (disk at 75%) 2. Navigate to /var/www/app (click through tree) 3. Double-click config.yml (opens in editor) 4. Edit and Ctrl+S to save (instant) 5. Go to Services section → Click "Restart" on app 6. Logs appear automatically in panel below 7. All in 30 seconds vs 2-3 minutes
Related guides:
- How to Manage a VPS Without Command Line
- Managing Docker Containers Without Command Line: Complete Guide
- Server Explorer vs Terminal SSH: Which One Should You Use?
File Management with SSH without Terminal
File operations are the most common server tasks—and the most painful in terminal.
Traditional Terminal File Management
Common file tasks require remembering many commands:
Navigate directories:
Copied!cd /var/www # Change directory ls -lah # List files (detailed, all, human-readable) pwd # Print working directory (where am I?)
Create/delete:
Copied!mkdir new-folder # Create directory touch new-file.txt # Create empty file rm -rf old-folder # Delete folder (dangerous!)
Edit files:
Copied!nano config.yml # Open in nano # Edit # Ctrl+X to exit # Y to confirm save # Enter to confirm filename
Permissions:
Copied!chmod 755 script.sh # Make executable chown user:group file.txt # Change owner
Search:
Copied!find / -name "*.conf" # Find all .conf files grep -r "error" /var/log/ # Search in logs
Upload/download:
Copied!scp local.txt user@server:/remote/path/ scp user@server:/remote/file.txt ./local/
Visual File Management Alternative
All above operations become:
Navigate: Click through folder tree
Create/delete: Right-click → New Folder/Delete
Edit: Double-click file → Edit → Ctrl+S to save
Permissions: Right-click → Permissions → Check boxes
Search: Type in search box → Results appear
Upload: Drag file from desktop to server folder
Download: Right-click → Download
File Management Workflow Comparison
Task: Edit nginx config, make it executable, restart nginx
Terminal SSH (6 steps, 2-3 minutes):
Copied!cd /etc/nginx/sites-available/ sudo nano my-site.conf # Edit file # Ctrl+X, Y, Enter to save sudo chmod 755 my-site.conf sudo systemctl restart nginx sudo systemctl status nginx
Visual SSH (3 steps, 30 seconds):
Copied!1. Navigate to /etc/nginx/sites-available/ 2. Edit my-site.conf → Save 3. Right-click → Permissions → Execute checkbox → Apply 4. Web panel → Nginx → Restart button
Time saved: 70%
Mental effort: Drastically reduced
Errors prevented: Visual confirmation at each step
Server Monitoring with SSH without Terminal
Understanding server health through terminal commands is challenging.
Terminal Monitoring Commands
Check various metrics sequentially:
Copied!# CPU usage top # (wait, observe, press 'q' to quit) # Memory usage free -h # Output: # total used free shared buff/cache available # Mem: 7.8Gi 2.1Gi 3.2Gi 234Mi 2.5Gi 5.2Gi # Disk space df -h # Output: # Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on # /dev/sda1 50G 32G 16G 68% / # Network connections netstat -tuln | grep LISTEN # System uptime uptime # 15:23:01 up 45 days, 3:12, 2 users, load average: 0.52, 0.58, 0.59 # Processes ps aux | grep node
Problems:
- Must run commands sequentially
- Text output hard to parse
- No historical trends
- No visual correlation between metrics
- Mental overhead to understand state
Visual Server Monitoring
Server Explorer dashboard shows simultaneously:
CPU Panel:
- Current usage percentage
Memory Panel:
- Used RAM (GB and %)
- Available RAM
Disk Space Panel:
- Used space per partition
- Visual bar graphs
- Percentage indicators
Network Panel:
- Inbound/outbound traffic
Process List:
- All processes with resource usage
- Sort by CPU or RAM
Monitoring Workflow Comparison
Task: “Why is my server slow?”
Terminal SSH investigation:
Copied!top # Is CPU high? free -h # Out of memory? df -h # Disk full? ps aux | head # What's using resources? # Mental correlation of all data # Takes 3-5 minutes
Visual SSH investigation:
Copied!Open dashboard → Immediately see: - CPU at 95% (red indicator) - RAM normal (green) - Disk okay (green) - Process "node-app" using 94% CPU (highlighted) - All in 5 seconds
Diagnosis time: 5 seconds vs 5 minutes

Docker Management via Visual SSH
Docker commands are powerful but verbose—visual alternatives simplify common operations.
Terminal Docker Management
Common Docker tasks via terminal:
List containers:
Copied!docker ps -a # Shows table, hard to read many containers
Check logs:
Copied!docker logs -f container_name # Follows logs, blocks terminal # Ctrl+C to exit
Restart container:
Copied!docker restart container_name docker ps | grep container_name # Verify it restarted
View resource usage:
Copied!docker stats # Real-time stats, but blocks terminal
Execute command in container:
Copied!docker exec -it container_name bash # Now you're inside container shell
Manage images/volumes/networks:
Copied!docker images docker volume ls docker network ls docker system prune # Cleanup
Visual Docker Management
Server Explorer Docker Manager provides:
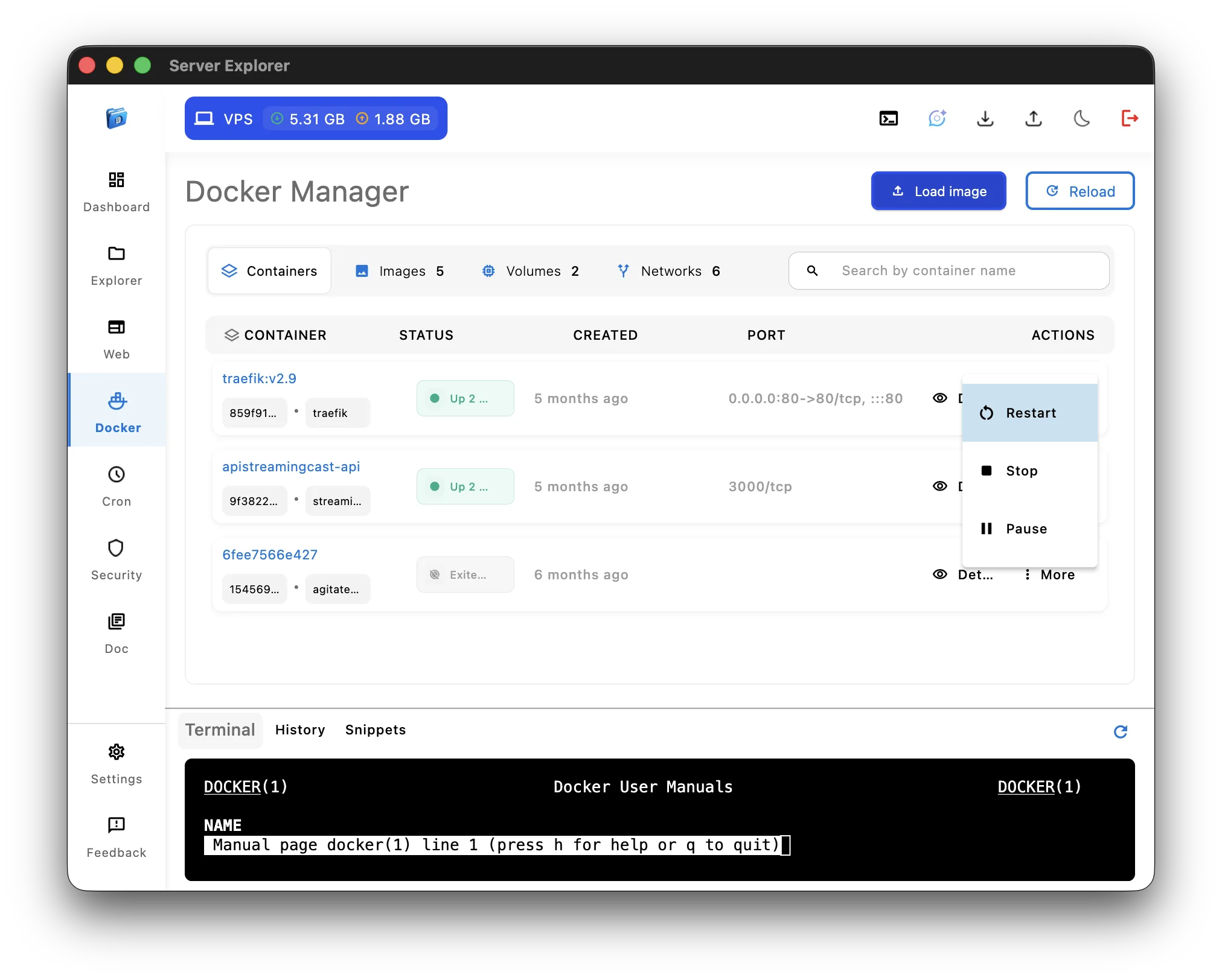
Container List:
- All containers with status (running/stopped)
- Resource usage per container (CPU/RAM)
- Uptime
- Port mappings
- One-click actions (Start, Stop, Restart, Delete)
Container Details:
- Environment variables (visual list)
- Volume mounts
- Network connections
- Exposed ports
- Live logs (auto-refreshing)
Container Filesystem:
- Browse files inside container
- Edit configuration files
- Download logs or generated files
Image Management:
- List all images with sizes
- Pull new images
- Delete unused images
- Tag images
Volume & Network Management:
- Visual list of volumes
Docker Workflow Comparison
Task: Restart problematic container and check logs
Terminal SSH:
Copied!docker ps -a | grep api # Find container ID: a1b2c3d4e5f6 docker restart a1b2c3d4e5f6 docker logs -f a1b2c3d4e5f6 # Read logs # Ctrl+C to exit docker ps | grep api # Verify running # Takes 1-2 minutes
Visual SSH (Server Explorer):
Copied!1. Open Docker section 2. Find "api" container in list (already visible) 3. Click "Restart" button 4. Open Container details 4. Logs appear automatically 5. Status shows "Running" with green indicator # Takes 10 seconds
Time saved: 90%
Related: Managing Docker Containers Without Command Line: Complete Guide
When Terminal SSH Still Makes Sense
Visual SSH tools are powerful, but terminal remains essential for certain tasks.
Tasks Better Suited for Terminal
1. Complex scripting and automation
Copied!# Deploy script for server in server{1..5}; do ssh $server "cd /app && git pull && pm2 restart all" done
Why terminal wins: Scripting languages, loops, conditionals
2. Git operations
Copied!git pull origin main git status git add . git commit -m "Update" git push
Why terminal wins: Git is fundamentally CLI-based.
But we are thinking about integrated a Git GUI in server explorer, sshhhht…. it’s our secret.
3. Package installation and updates
Copied!sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade -y sudo apt install nginx mysql-server php8.1
Why terminal wins: Package managers are terminal-native
4. Complex text processing
Copied!grep "error" /var/log/app.log | awk '{print $1, $5}' | sort | uniq -c
Why terminal wins: Pipes, grep, awk, sed are irreplaceable
5. System administration scripts
Copied!# Backup script tar -czf backup-$(date +%Y%m%d).tar.gz /var/www rsync -avz backup-*.tar.gz user@backup-server:/backups/
Why terminal wins: Shell scripting for complex automation
The Hybrid Approach (Best Practice)
Use visual SSH for:
- Daily server monitoring
- File browsing and editing
- Docker container management
- Quick permission changes
- Visual log inspection
- Learning and exploration
Use terminal SSH for:
- Git operations
- Package management
- Complex scripting
- Text processing pipelines
- Automation tasks
- One-off complex commands
Server Explorer provides both: Visual tools for 80% of tasks, integrated terminal for the other 20%.
For more on balancing approaches, see: Server Explorer vs Terminal SSH: Which One Should You Use?
Advantages of Visual SSH Over Terminal
1. Reduced Cognitive Load
Terminal requires:
- Remembering command syntax
- Recalling file paths
- Understanding text output
- Mental state tracking (where am I? what did I just do?)
Visual SSH provides:
- Point and click
- Visual location awareness
- Graphical feedback
- Clear current state
Result: Mental energy freed for actual problem-solving
2. Faster Common Operations
80% of server management is repetitive:
- Check if app is running
- Edit configuration file
- Restart service
- Check logs
- View disk space
These tasks are 5-10x faster visually:
- Click vs. type command
- See vs. parse text output
- Button vs. systemctl command
3. Lower Error Rate
Terminal errors:
- Typos in commands (rm -rf vs rm -rf /)
- Wrong directory (edited wrong config file)
- Permission errors (forgot sudo)
- Syntax mistakes (chmod 644 instead of 755)
Visual interfaces prevent:
- Typos (no typing commands)
- Wrong location (see where you are)
- Permission handling (automatic sudo prompt)
- Syntax errors (validated inputs)
4. Better Learning Experience
Terminal learning:
- Steep curve (must memorize before doing)
- Trial and error (break things to learn)
- Documentation-heavy (constant googling)
Visual learning:
- Gentle curve (explore by clicking)
- Safe experimentation (visual confirmation)
- Discoverable (see options available)
- Gradual CLI introduction (integrated terminal)
5. Parallel Information Display
Terminal shows information sequentially:
Copied!Command 1 → Output 1 Command 2 → Output 2 Command 3 → Output 3
Visual interfaces show simultaneously:
Copied!┌─────────┬─────────┬─────────┐ │ CPU 45% │ RAM 60% │ Disk 75%│ ├─────────┴─────────┴─────────┤ │ Container List (5 running)│ │ Process List (sorting CPU)│ │ Live Logs (auto-scrolling)│ └──────────────────────────────┘
Result: Faster correlation, quicker problem diagnosis
Common Objections to Visual SSH
“Terminal is faster once you learn it”
Reality: For specialized tasks (scripting, pipelines), yes. For daily operations (file editing, monitoring, service restarts), visual is faster even for experts.
Analogy: Professional photographers still use auto modes when appropriate, even though they know manual settings.
“I need to know terminal for interviews/jobs”
Reality: Visual tools help you learn terminal better by showing the relationship between actions and commands. You’re not replacing knowledge—you’re building it more efficiently.
“Real sysadmins use terminal only”
Reality: Professional sysadmins use the best tool for each task. Many use Grafana (visual monitoring), Portainer (visual Docker), and other GUIs alongside terminal. Tool choice is about efficiency, not identity.
Conclusion
SSH without terminal is not only possible—it’s often better for daily server management.
Visual SSH tools like Server Explorer provide:
✅ Lower barrier to entry – Manage servers without memorizing commands
✅ Faster routine operations – Click vs. type for common tasks
✅ Better visibility – See everything at once, not sequentially
✅ Reduced errors – Visual confirmation before actions
✅ Learning aid – Understand Linux visually while building CLI skills
✅ Same security – Uses standard SSH protocol
✅ Hybrid approach – Visual tools + integrated terminal
You’re not avoiding SSH—you’re using it more efficiently.
When to Choose Visual SSH
Visual SSH tools are ideal if you:
- Manage Linux VPS servers regularly
- Want faster file editing workflows
- Prefer visual monitoring dashboards
- Need Docker or PM2 management
- Are learning Linux administration
- Value time-saving workflows
- Want security scanning automation
Terminal SSH remains essential for:
- Complex scripting and automation
- Git operations
- Package management
- Text processing pipelines
- CI/CD integration
The best approach? Hybrid. Use visual tools for 80% of daily tasks, terminal for the remaining 20%.
Experience SSH Without Terminal Today
Ready to manage Linux servers visually while maintaining SSH security?

Try Server Explorer Today
Manage your servers with just a few clicks. Replace complex command-line operations with an intuitive interface, while maintaining the performance and security of traditional SSH access.
What you get:
✅ Visual file browser with direct editing
✅ Server dashboard (CPU/RAM/disk monitoring)
✅ Docker container management
✅ PM2 process monitoring
✅ Security scanner (18 automated checks)
✅ Cron job scheduler
✅ Integrated SSH terminal
✅ Multi-server management
Available for Windows and macOS
No terminal commands required. Full SSH security maintained.
